Facilities
Caltech Ludwieg Tube

When using the Mach 2.3 Nozzle an aluminum diaphragm is inserted between the test section and the dump tank. The dump tank is evacuated and the driver tube, nozzle, and test section are pressurized to the desired fill pressure, typically 2-5 bar, and a pneumatic cylinder drives a sharp diaphragm-breaker into the diaphragm from behind to start the run. When the diaphragm ruptures a weak shock propagates into the dump tank and a nonsteady expansion wave propagates upstream into the driver tube. The expansion wave sets up steady flow through the nozzle and test section until the wave returns to the entrance of the nozzle after reflecting off of the driver tube end-wall.
Because of the higher pressure ratio required to sustain steady supersonic flow through a converging-diverging nozzle at Mach 4 compared to Mach 2.3, it is not possible to start the Ludwieg tube using a diaphragm downstream of the nozzle using the Mach 4 nozzle due to sizing of the dump tank and pressure limitations of the driver tube. A diaphragm upstream of the nozzle was used instead from 2004 until 2014. After improvements to the schlieren visualization setup and a decision to study boundary layer instabilities in the Ludwieg tube the need for an alternative method was realized because the diaphragm was observed to produce significant additional freestream noise in the test section.
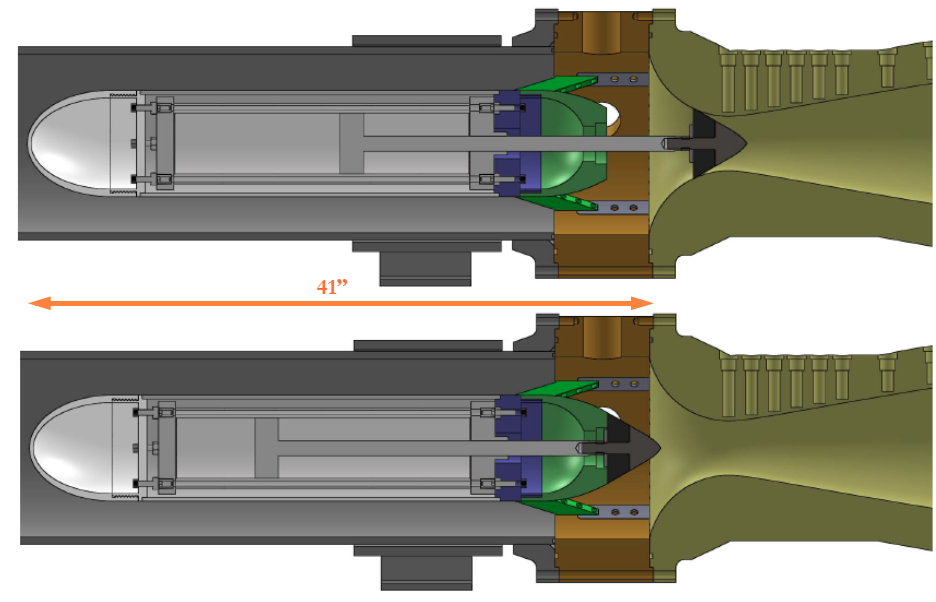
The current method for starting the Ludwieg tube is to use a nozzle throat plug connected to a pneumatic cylinder. The plug begins in the throat of the nozzle while the dump tank, test section, and nozzle are evacuated and the driver tube is pressurized. To start a run the pneumatic cylinder pulls the plug out of the nozzle in about 20 ms which allows compression waves to form a shock that propagates through the nozzle and test section and a train of expansion waves to propagate upstream into the driver tube. This method reduces the noise in the freestream and also reduces turnaround time between runs to about 15 minutes. The only disadvantage to this method is that the test time is reduced to about 50 ms. A solid model showing the plug in the closed (top) and open (bottom) position is shown below.